The Valencia Diet: A Comprehensive Guide to Healthy Eating
The Valencia Diet is a nutritional regimen inspired by the culinary traditions of Valencia, a vibrant region on Spain’s eastern coast. Known for its rich history, diverse cuisine, and emphasis on fresh, locally sourced ingredients, the Valencia Diet offers a unique approach to healthy eating that combines traditional Mediterranean principles with modern nutritional insights.
In a world increasingly plagued by diet-related health issues, the Valencia Diet stands out for its potential to promote overall well-being. This diet is characterized by a balanced intake of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, making it delicious and highly beneficial for maintaining optimal health.
Key Components of the Valencia Diet
Emphasis on Fresh, Local Produce

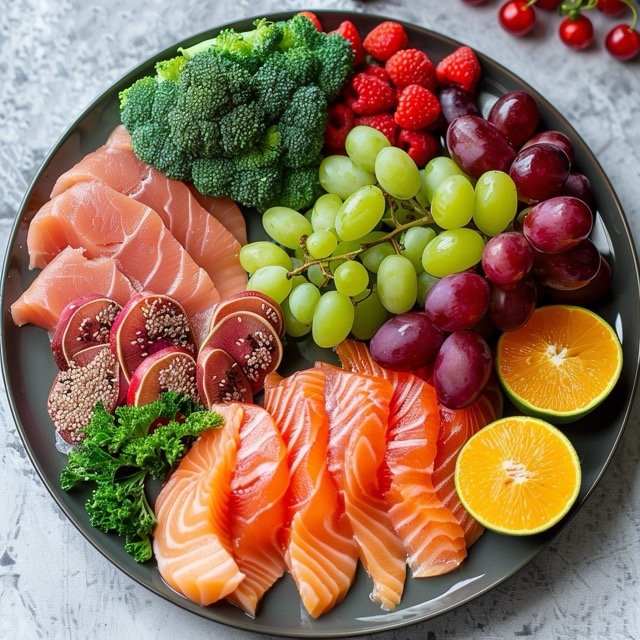
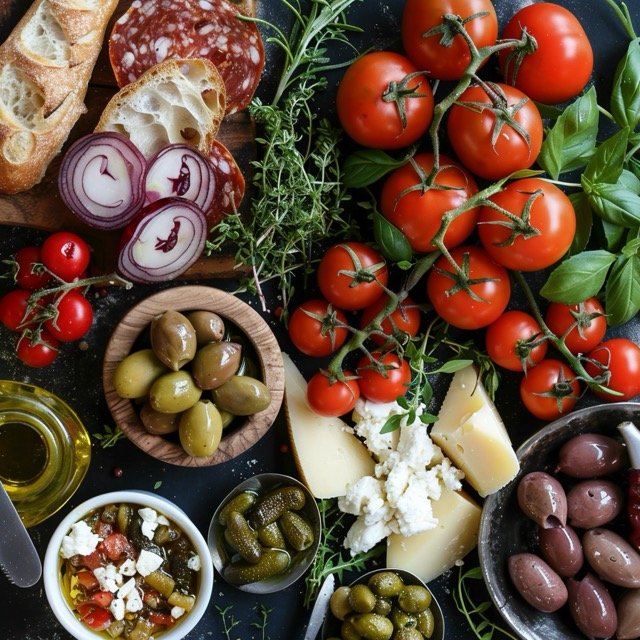
- Fruits and Vegetables: The Valencia Diet centers on the abundant consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables. Valencian cuisine often features produce such as tomatoes, peppers, onions, and oranges. These ingredients are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are essential for preventing chronic diseases and boosting the immune system.
- Example: A traditional Valencian salad, known as “Ensalada Valenciana,” includes a variety of fresh vegetables like tomatoes, onions, and olives, dressed with olive oil and vinegar. This dish is nutrient-dense and flavorful.
Incorporation of Lean Proteins
- Seafood: Given Valencia’s coastal location, seafood plays a significant role in the local diet. Fish such as sardines, mackerel, and cod are common, offering high-quality protein and omega-3 fatty acids that support heart health.
- Example: The famous “Paella Valenciana,” a rice dish that includes a mix of seafood like mussels, shrimp, and clams, along with chicken and rabbit, is a perfect representation of this dietary component.
Use of Healthy Fats
- Olive Oil: A staple in Mediterranean diets, olive oil is the primary fat used in the Valencia Diet. It is known for its heart-protective properties and ability to reduce inflammation.
- Example: Drizzling extra virgin olive oil over roasted vegetables or using it as a base for homemade salad dressings is a common practice in Valencian cuisine.
Whole Grains and Legumes

- Grains: Whole grains such as brown rice, barley, and whole wheat are favored over refined grains. These provide essential nutrients and help maintain steady blood sugar levels.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are integral to the diet, offering fiber, protein, and various micronutrients.
- Example: “Fesols i Naps,” a traditional Valencian stew made with beans and turnips, showcases the use of legumes in hearty, nutritious meals.
Moderate Dairy Consumption
- Dairy: While dairy is not a primary focus, moderate consumption of yogurt and cheese is included, providing calcium and probiotics beneficial for gut health.
- Example: A serving of “Horchata,” a traditional Valencian drink made from tiger nuts, can be paired with a small portion of cheese for a balanced snack.
Health Benefits and Supporting Data
Cardiovascular Health
- Studies: Research has shown that diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, like the Valencia Diet, can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. A study published in the “New England Journal of Medicine” highlighted the Mediterranean diet’s effectiveness in reducing heart disease risk by up to 30%.
Weight Management

- Data: The balanced nature of the Valencia Diet, with its emphasis on whole foods and lean proteins, supports healthy weight management. According to a study in the “Journal of Nutrition,” individuals following a Mediterranean-style diet experienced greater weight loss and improved metabolic health compared to those on a low-fat diet.
Diabetes Prevention
- Statistics: The high fiber content from fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes helps regulate blood sugar levels and can prevent type 2 diabetes. A “American Journal of Clinical Nutrition” review found that high-fiber diets reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 30-50% (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov – Dietary Fiber Intake and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus).
Practical Implementation
Meal Planning Tips
- Seasonal Eating: Emphasize seasonal produce to maximize nutrient intake and flavor. For instance, in summer, focus on tomatoes, zucchini, and melons, while in winter, incorporate root vegetables and citrus fruits.
- Cooking Methods: Grilling, roasting, and steaming are recommended over frying to save the nutritional value of the ingredients.
Sample Meal Plan

- Breakfast: Greek yogurt with fresh berries and a drizzle of honey.
- Lunch: Mixed green salad with grilled chicken, tomatoes, cucumbers, and a lemon-olive oil dressing.
- Dinner: Grilled fish with a side of quinoa and roasted vegetables.
- Snacks: Fresh fruit, nuts, or a small serving of cheese.
Conclusion
The Valencia Diet offers a delicious and sustainable approach to healthy eating rooted in Valencia’s rich culinary traditions. Focusing on fresh, local produce, lean proteins, healthy fats, and whole grains can significantly improve overall health and well-being.
To explore the Valencia Diet further, consider trying some traditional recipes or consult a nutritionist to tailor the diet to your specific needs. Embracing this diet could lead to a healthier, more vibrant lifestyle.
By incorporating these elements into your daily routine, you can enjoy the numerous health benefits of the Valencia Diet. Specialized cookbooks and online culinary guides offer additional resources and detailed recipes for those interested in delving deeper. As always, you can visit us at FittBeat to become serious about changing your health.