Paleo Diet: Can You Eat Like a Caveman and Lose Weight?
The Paleo Diet, often called the “caveman diet,” has recently garnered significant attention for its back-to-basics nutrition approach. Rooted in the dietary habits of our Paleolithic ancestors, this diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods that early humans would have consumed. The premise is straightforward: by mimicking the diet of our hunter-gatherer forebears, we can achieve better health, weight management, and overall well-being.
Why is the Paleo Diet relevant in today’s health-conscious world? Modern diets are often laden with processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats, contributing to a myriad of health issues such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. The Paleo Diet offers a potential remedy by promoting natural, nutrient-dense foods to help individuals achieve optimal health.
Key Principles of the Paleo Diet
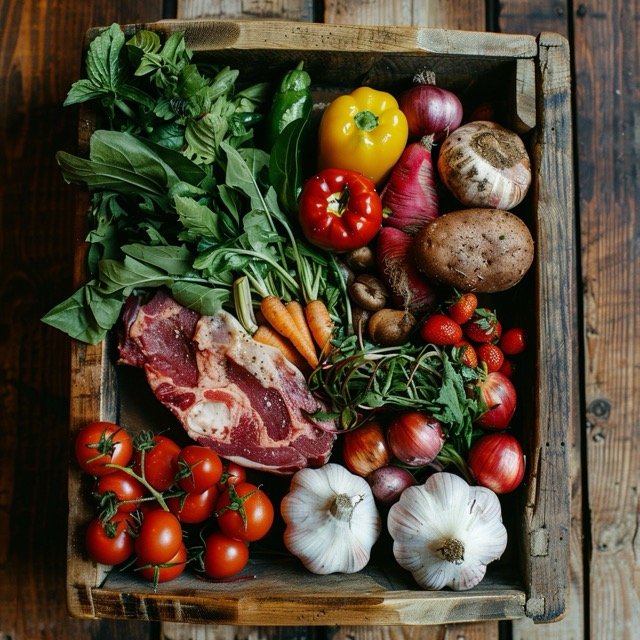

The Paleo Diet is centered around several key principles that differentiate it from other dietary approaches. These principles are designed to align our eating habits more closely with those of our ancestors, promoting a diet that is rich in nutrients and free from processed ingredients.
1. Whole Foods Emphasis
The cornerstone of the Paleo Diet is the consumption of whole foods. This includes:
- Lean Meats: Grass-fed beef, poultry, pork, and game meats.
- Fish and Seafood: Salmon, mackerel, and other wild-caught fish.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Berries, leafy greens, and root vegetables.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and sunflower seeds.
- Healthy Fats: Avocado, olive oil, and coconut oil.
By focusing on whole foods, the Paleo Diet eliminates processed foods that often contain artificial additives, preservatives, and unhealthy trans fats.
2. High Protein Intake
Protein is a vital component of the Paleo Diet, reflecting the hunter-gatherer reliance on animal-based foods. High protein intake supports muscle growth, repair, and satiety, helping to maintain lean body mass and control hunger.
- Practical Example: A typical Paleo meal might include grilled chicken breast with roasted vegetables on the side and a mixed green salad.
3. Low Carbohydrate Consumption
While the Paleo Diet is not strictly low-carb, it naturally reduces carbohydrate intake by excluding grains and refined sugars. This can help stabilize blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Practical Example: Instead of a sandwich, a Paleo-friendly lunch might consist of a large salad with mixed greens, vegetables, grilled chicken, and a dressing made from olive oil and lemon juice.
Benefits of the Paleo Diet

Adopting this Diet can offer numerous health benefits, supported by both anecdotal evidence and scientific research.
1. Weight Loss and Management
The Paleo Diet’s emphasis on nutrient-dense, whole foods can lead to natural weight loss and improved body composition. A study published in the journal Obesity found that participants on this diet lost more weight and inches around their waist than those on a standard diet.
2. Improved Blood Sugar Control
The Paleo Diet can help manage blood sugar levels by reducing refined carbohydrates and sugars. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance. Research in the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition demonstrated that the Paleo Diet improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in healthy volunteers.
3. Enhanced Satiety
The high protein and fiber content of the Paleo Diet can increase feelings of fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating and snacking on unhealthy foods. This can contribute to better appetite control and long-term weight management.
4. Reduced Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is linked to numerous health issues, including heart disease and autoimmune disorders. The anti-inflammatory properties of the Paleo Diet, due to its high intake of omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants from fruits and vegetables, can help reduce inflammation markers in the body.
Potential Drawbacks of the Paleo Diet

While the Paleo Diet has many advocates, it is not without its criticisms and potential downsides. Considering these factors before fully committing to this dietary approach is essential.
1. Nutrient Deficiencies
Excluding entire food groups, such as dairy and grains, can lead to nutrient deficiencies if not carefully managed. For example:
- Calcium: Dairy is a primary source of calcium, essential for bone health. Without it, individuals may need to rely on alternative sources like leafy greens or supplements.
- Fiber: Grains are rich in dietary fiber, which is important for digestive health. The Paleo Diet requires individuals to get sufficient fiber from fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
2. High Cost
The emphasis on organic, grass-fed, and wild-caught foods can make the Paleo Diet more expensive than conventional diets. This can be a barrier for some people looking to adopt this way of eating.
3. Social and Practical Challenges
The restrictive nature of this Diet can make social situations and dining out more challenging. It requires careful planning and preparation, which can be time-consuming and difficult to maintain long-term.
Paleo Diet Sample Meal Plan
Sure! Here is a sample Paleo diet meal plan for two days, including breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks.
Day 1
Breakfast
- Vegetable Omelette
- 3 eggs
- 1/2 cup of chopped spinach
- 1/4 cup of diced bell peppers
- 1/4 cup of diced onions
- 1 tablespoon of olive oil
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions: Sauté the vegetables in olive oil until soft. Whisk the eggs, pour over the vegetables, and cook until set.
Snack
- Mixed Nuts and Berries
- 1/4 cup of mixed nuts (almonds, walnuts, cashews)
- 1/2 cup of mixed berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries)
Lunch
- Grilled Chicken Salad
- 1 grilled chicken breast, sliced
- 2 cups of mixed greens (lettuce, spinach, arugula)
- 1/2 cup of cherry tomatoes, halved
- 1/4 cup of sliced cucumbers
- 1/4 avocado, sliced
- 2 tablespoons of olive oil
- 1 tablespoon of balsamic vinegar
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions: Combine all salad ingredients and drizzle with olive oil and balsamic vinegar.
Snack
- Apple Slices with Almond Butter
- 1 medium apple, sliced
- 2 tablespoons of almond butter
Dinner
- Baked Salmon with Asparagus
- 1 salmon fillet
- 1 cup of asparagus spears
- 1 tablespoon of olive oil
- Lemon juice
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions: Preheat oven to 400°F (200°C). Place the salmon fillet and asparagus on a baking sheet. Drizzle with olive oil, lemon juice, salt, and pepper. Bake for 15-20 minutes until the salmon is cooked through.
Day 2
Breakfast
- Banana Nut Porridge
- 1 banana, mashed
- 1/4 cup of almond flour
- 1/4 cup of coconut milk
- 1 tablespoon of chia seeds
- 1/2 teaspoon of cinnamon
- 1 tablespoon of chopped nuts (almonds, walnuts)
Instructions: Combine mashed banana, almond flour, coconut milk, chia seeds, and cinnamon in a saucepan. Cook over medium heat until thickened. Top with chopped nuts.
Snack
- Carrot Sticks with Guacamole
- 1 cup of carrot sticks
- 1/2 cup of guacamole
Lunch
- Turkey Lettuce Wraps
- 4 large lettuce leaves
- 1 cup of cooked ground turkey
- 1/4 cup of diced tomatoes
- 1/4 cup of diced bell peppers
- 1/4 cup of diced onions
- 1 tablespoon of olive oil
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions: Sauté the ground turkey with diced vegetables in olive oil until fully cooked. Season with salt and pepper. Spoon the turkey mixture into lettuce leaves and wrap.
Snack
- Cucumber Slices with Tuna Salad
- 1 cup of cucumber slices
- 1 can of tuna, drained
- 2 tablespoons of mayonnaise (Paleo-friendly)
- 1 tablespoon of diced celery
- 1 tablespoon of diced onions
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions: Mix the tuna with mayonnaise, celery, and onions. Season with salt and pepper. Serve with cucumber slices.
Dinner
- Beef and Vegetable Stir-Fry
- 1 cup of sliced beef (sirloin or flank steak)
- 1 cup of broccoli florets
- 1/2 cup of sliced bell peppers
- 1/2 cup of snap peas
- 1 tablespoon of coconut aminos (soy sauce alternative)
- 1 tablespoon of coconut oil
- 1 garlic clove, minced
- 1 teaspoon of grated ginger
Instructions: Heat coconut oil in a large pan over medium-high heat. Add beef slices and cook until browned. Remove beef and set aside. In the same pan, add garlic and ginger, then vegetables. Stir-fry until vegetables are tender. Return beef to the pan, add coconut aminos, and stir until well combined.
This two-day Paleo meal plan provides a variety of nutrient-dense, delicious meals that align with Paleo principles. Adjust portion sizes and ingredients to suit personal preferences and dietary needs.
Case Studies and Data
Case Study: Weight Loss Success
A case study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition followed a group of individuals over six months. Compared to those on a standard diet, participants who adhered to the Paleo Diet experienced significant weight loss, reduced waist circumference, and improved metabolic health markers.
Research Data: Health Benefits
A Journal of Internal Medicine meta-analysis reviewed multiple studies on the Paleo Diet. The analysis concluded that the diet could improve weight, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, and blood pressure, supporting the diet’s potential health benefits.
Conclusion
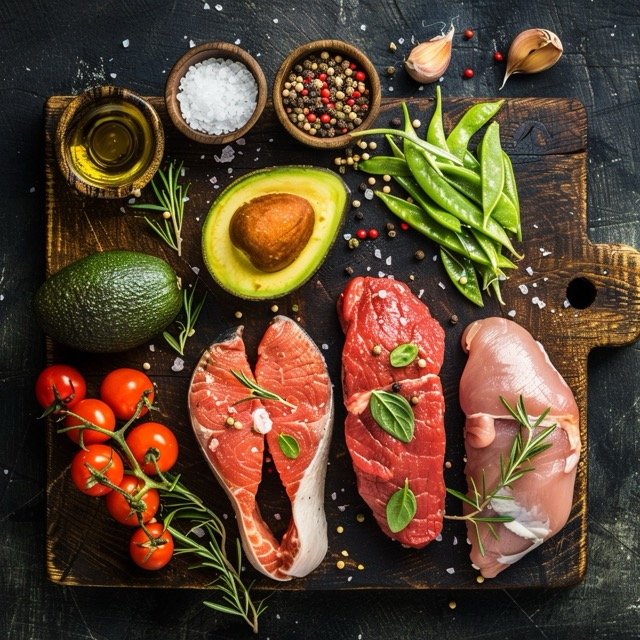

The Paleo Diet offers a compelling approach to nutrition by focusing on whole, unprocessed foods that our ancestors would have consumed. It provides numerous health benefits, including weight loss, improved blood sugar control, enhanced satiety, and reduced inflammation. However, it is important to be aware of potential drawbacks, such as nutrient deficiencies, higher costs, and social challenges.
For those considering the Paleo Diet, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to ensure it meets their nutritional needs and lifestyle. Further reading and resources, such as books, reputable websites like us at FittBeat, and support groups, can provide additional guidance and support.
Suggested Further Reading
- The Paleo Diet by Dr. Loren Cordain- 4.3 Stars on Amazon
- Practical Paleo by Diane Sanfilippo- 4.6 Stars on Amazon
- PaleoLeap.com – A comprehensive resource for Paleo recipes and tips
By understanding both the benefits and challenges, individuals can make an informed decision about whether this Diet is the right choice for their health and wellness goals.
Sources and Citations
- Obesity: Study on Weight Loss and Paleo Diet
- European Journal of Clinical Nutrition: Research on Blood Sugar Control
- The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition: Case Study on Weight Loss Success
- Journal of Internal Medicine: Meta-Analysis on Paleo Diet Benefits
This comprehensive review of the Paleo Diet aims to provide a balanced perspective, highlighting both its advantages and potential drawbacks. By presenting well-researched information and practical examples, this article seeks to engage and inform readers considering this dietary approach.