Keto Diet Review: The Ultimate Guide to Losing 20 Pounds
The ketogenic diet, commonly known as the Keto Diet, has surged in popularity over recent years, capturing the attention of those seeking effective weight loss strategies and improved health.
This low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet is designed to push the body into a metabolic state called ketosis, where fats are burned for energy instead of carbohydrates.
This comprehensive review will explore the principles of the Keto Diet, its benefits, potential drawbacks, and the scientific evidence supporting its use.
Understanding the Keto Diet
The Keto Diet involves a significant reduction in carbohydrate intake and increased fats. Typically, the macronutrient breakdown is as follows:
- Carbohydrates: 5-10% of daily intake
- Proteins: 20-25% of daily intake
- Fats: 70-75% of daily intake
This drastic shift in macronutrient consumption forces the body to use fat as its primary energy source, leading the liver to produce ketones. Ketones are an alternative fuel source, especially beneficial for the brain.
Benefits of the Keto Diet
Weight Loss
- Mechanism: By reducing carbohydrate intake, insulin levels drop, leading to the breakdown of fat stores and increased fat burning.
- Evidence: Studies have shown that individuals on a ketogenic diet can lose more weight compared to those on low-fat diets. A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that participants on a ketogenic diet lost more weight over 24 weeks than those following a low-fat diet.
Improved Blood Sugar Control
- Mechanism: Lower carbohydrate intake reduces blood sugar levels, benefiting individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- Evidence: A study in Diabetes Therapy demonstrated that a ketogenic diet improved glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes, reducing their reliance on medication. (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30289048/)
Enhanced Mental Clarity and Focus
- Mechanism: Ketones are a more efficient fuel for the brain than glucose, leading to improved cognitive function.
- Evidence: Research in the Neurobiology of Aging indicates that the ketogenic diet may enhance cognitive performance in older adults with a high risk of Alzheimer’s disease. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6356942/)
Increased Energy and Reduced Hunger
- Mechanism: Fats are more satiating than carbohydrates, which can reduce overall calorie intake and suppress appetite.
- Evidence: A study in Obesity found that participants on a ketogenic diet reported reduced hunger and a lower desire to eat, contributing to weight loss and maintenance.
Practical Examples and Tips
- Meal Planning: Typical keto meals include eggs and bacon for breakfast, a salad with avocado and grilled chicken for lunch, and a dinner of salmon with a side of broccoli cooked in olive oil.
- Snack Options: Keto-friendly snacks include cheese, nuts, seeds, and low-carb vegetables with dip.
- Dining Out: Many restaurants now offer keto-friendly options such as bunless burgers, grilled meats, and salads with high-fat dressings.
3-Day Sample Keto Meal Plan
Here’s a detailed 3-day meal plan to help you start your keto journey. Each day includes breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks that adhere to the keto macronutrient guidelines.
Day 1

Breakfast– Keto Scrambled Eggs
- 2 large eggs
- 2 tablespoons heavy cream
- 1 tablespoon butter
- 1/4 cup shredded cheddar cheese
- Salt and pepper to taste
Snack– Avocado
- 1/2 avocado
- Sprinkle with salt, pepper, and a squeeze of lemon juice
Lunch– Chicken Caesar Salad
- 2 cups Romaine lettuce, chopped
- 1 grilled chicken breast, sliced
- 2 tablespoons Caesar dressing (low-carb)
- 1 tablespoon grated Parmesan cheese
- 1/4 cup bacon bits
Snack– Cucumber Slices with Cream Cheese
- 1 cup cucumber slices
- 2 tablespoons cream cheese
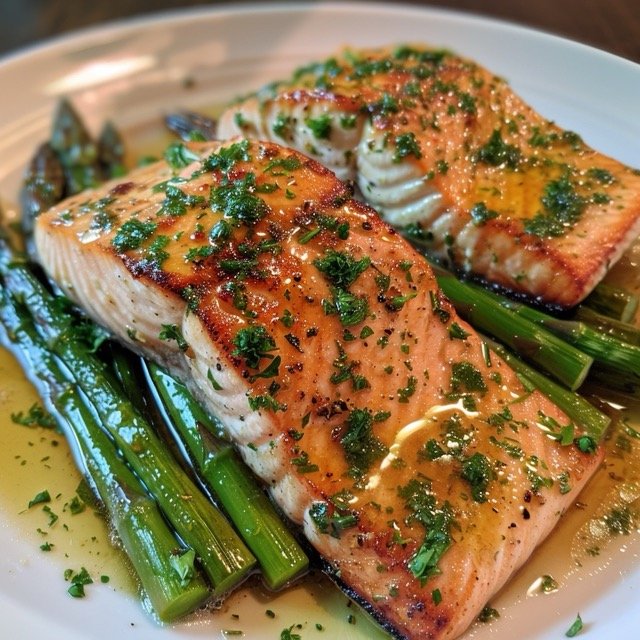
Dinner– Garlic Butter Salmon with Asparagus
- 1 salmon fillet
- 1 tablespoon butter
- 1 garlic clove, minced
- 1 cup asparagus, steamed
- Lemon wedges for garnish
Day 2
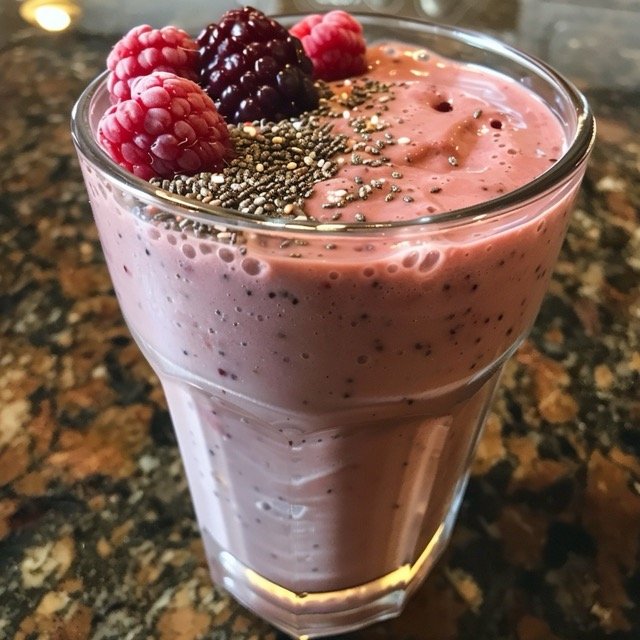

Breakfast– Keto Smoothie
- 1 cup unsweetened almond milk
- 1/2 cup frozen berries (strawberries, raspberries)
- 1 tablespoon chia seeds
- 1 tablespoon almond butter
Snack– Cheese and Nuts
- 1 ounce cheddar cheese
- 1/4 cup almonds
Lunch– Turkey Lettuce Wraps
- 4 large lettuce leaves
- 4 slices turkey breast
- 1/4 avocado, sliced
- 1/4 cup shredded cheese
- 2 tablespoons mayonnaise (Chosen Foods Traditional Keto Mayo)
Snack- Olives and Pickles
- 1/4 cup green olives
- 1/4 cup pickles
Dinner- Zucchini Noodles with Pesto and Grilled Chicken
- 1 large zucchini, spiralized
- 1 grilled chicken breast, sliced
- 2 tablespoons pesto sauce (low-carb)
- 1 tablespoon olive oil
Day 3
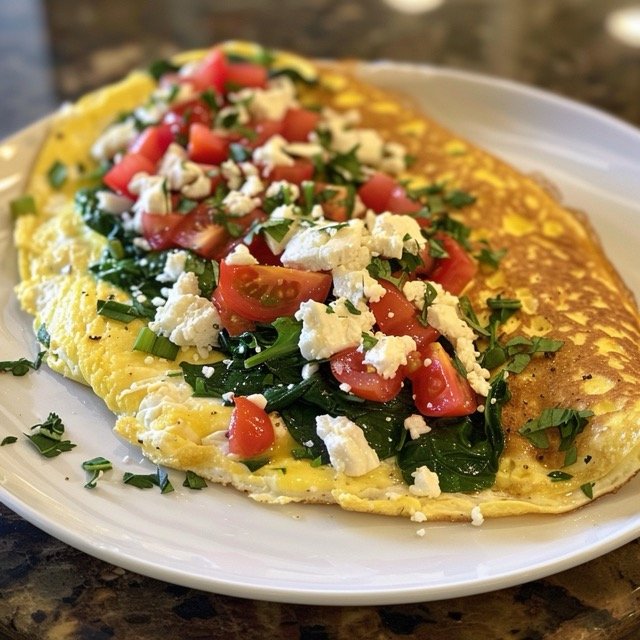

Breakfast- Keto Omelette
- 3 large eggs
- 1/4 cup chopped spinach
- 1/4 cup diced tomatoes
- 1/4 cup feta cheese
- 1 tablespoon olive oil
Snack- Pepperoni Slices
- 10 slices of pepperoni
- 1 string cheese
Lunch– Tuna Salad
- 1 can tuna, drained
- 2 tablespoons mayonnaise
- 1 celery stalk, diced
- 1 tablespoon diced red onion
- Salt and pepper to taste
- Lettuce leaves for serving
Snack- Celery with Peanut Butter
- 2 celery sticks
- 2 tablespoons natural peanut butter
Dinner- Beef and Broccoli Stir-Fry
- 1 cup beef strips
- 1 cup broccoli florets
- 1 tablespoon soy sauce
- 1 tablespoon olive oil
- 1 garlic clove, minced
- 1 teaspoon grated ginger
Tips for Following the Keto Diet
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated.
- Electrolytes: Ensure adequate sodium, potassium, and magnesium intake to prevent the “keto flu.”
- Meal Prep: Prepare meals and snacks in advance to avoid high-carb temptations.
- Reading Labels: Always check the nutritional information of packaged foods to ensure they fit within your daily carb limits.
By following this meal plan, you can start experiencing the benefits of the ketogenic diet while enjoying various delicious and satisfying meals.
Potential Drawbacks of the Keto Diet
Keto Flu
- Description: As the body transitions into ketosis, some individuals experience symptoms such as headache, fatigue, dizziness, and nausea, collectively known as the “keto flu.” (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7082414/)
- Mitigation: Staying hydrated, replenishing electrolytes, and gradually reducing carbohydrate intake can help alleviate these symptoms.
Nutrient Deficiencies
- Risk: Restricting certain food groups can lead to deficiencies in essential nutrients such as fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Solution: Incorporating a variety of low-carb vegetables, nuts, and seeds and taking a multivitamin supplement can help mitigate these risks.
Digestive Issues
- Symptoms: Some people may experience constipation or diarrhea due to changes in fiber intake and gut flora.
- Management: Increasing water intake, eating high-fiber keto-friendly foods, and considering probiotics can support digestive health.
Long-Term Sustainability
- Challenge: The restrictive nature of the Keto Diet can be challenging to maintain long-term, potentially leading to diet fatigue and relapse.
- Approach: Integrating occasional carb refeeds or transitioning to a more flexible low-carb diet after reaching health goals can improve sustainability.
Scientific Data and Case Studies
Epilepsy Management
- Background: The ketogenic diet was originally developed in the 1920s to treat epilepsy in children who did not respond to conventional treatments.
- Evidence: Research in The Lancet Neurology shows that the Keto Diet can significantly reduce seizure frequency in children with refractory epilepsy.
Cardiovascular Health
- Debate: There is ongoing debate about the impact of the Keto diet’s high-fat content on heart health.
- Study: A study in Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Obesity suggests that the diet can improve cardiovascular risk factors such as cholesterol levels, provided that healthy fats are chosen over saturated and trans fats.
Cancer Treatment
- Theory: Some researchers propose that the ketogenic diet may starve cancer cells of glucose, slowing tumor growth.
- Research: Preliminary studies, such as those published in Nutrition & Metabolism, indicate potential benefits, but more extensive human trials are needed to confirm these findings.
Conclusion
The Keto Diet offers a range of benefits, including weight loss, improved blood sugar control, enhanced mental clarity, and increased energy. However, it has challenges, such as the initial adjustment period, potential nutrient deficiencies, and long-term sustainability concerns.
For those considering the Keto Diet, it is essential to approach it with a well-informed perspective, possibly under the guidance of a healthcare provider or nutritionist. Further reading on keto recipes, meal planning, and success stories can provide additional support and motivation. FittBeat will provide some of this here on our site, but you can also use the resources below as well.
Suggested Further Reading
- Books: “The Art and Science of Low Carbohydrate Living” by Dr. Jeff Volek and Dr. Stephen Phinney
- Websites:
- Ruled.me
- Diet Doctor
- Scientific Journals: Access studies on the ketogenic diet through databases like PubMed for the latest research and developments.
By understanding the intricacies of the Keto Diet and preparing for its potential challenges, individuals can make an informed decision about whether this dietary approach aligns with their health goals and lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the rules of a Keto diet?
- – High Fat, Moderate Protein, Low Carb: 70-75% calories from fats, 20-25% from protein, 5-10% from carbs.
- – Limit carbs to less than 20-50 grams per day.
- – Eat unprocessed, whole foods like meats, fish, eggs, low-carb veggies, nuts, and seeds.
- – Stay hydrated and manage keto flu symptoms by drinking plenty of water.
- – Maintain electrolyte balance with adequate sodium, potassium, and magnesium intake.
- – Avoid sugary foods and drinks like sodas, candies, and desserts.
- – Prioritize healthy fats such as olive oil, avocado oil, coconut oil, butter, and ghee.
- – Be mindful of protein intake to prevent disruption of ketosis.
- – Choose keto-friendly snacks like cheese, nuts, and seeds.
- – Plan meals in advance to stay within macro limits and make healthy choices.
What foods are not allowed in Keto?
- Sugary Foods: Candies, cakes, cookies, ice cream, and sugary drinks.
- Grains and Starches: Bread, pasta, rice, cereal, and other grain-based foods.
- High-Carb Fruits: Bananas, apples, oranges, and most other fruits.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas.
- Root Vegetables: Potatoes, sweet potatoes, carrots, and other starchy vegetables.
- Low-Fat and Diet Products: These often contain added sugars.
- Some Condiments and Sauces: Ketchup, barbecue sauce, and some salad dressings due to their sugar content.
- Unhealthy Fats: Processed vegetable oils, mayonnaise, and margarine.Alcohol: Beer, sugary cocktails, and sweet wines.
- Processed Foods: Foods with added sugars, trans fats, or other additives.
What are the top 10 keto foods?
- Avocados: High in healthy fats and low in carbs, avocados are a staple in the keto diet.
- Eggs: Rich in protein and healthy fats, eggs are versatile and perfect for keto meals.
- Cheese: Full-fat cheeses are low in carbs and high in fat, making them ideal for keto.
- Meat and Poultry: Unprocessed meats and poultry are great sources of protein and contain no carbs.
- Fish and Seafood: Especially fatty fish like salmon, which is rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds provide healthy fats and are low in carbs.
- Olive Oil and Coconut Oil: Excellent sources of healthy fats for cooking and dressings.
- Low-Carb Vegetables: Leafy greens, zucchini, bell peppers, and broccoli are nutrient-dense and low in carbs.
- Berries: Small portions of strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries can be enjoyed on keto.
- Butter and Cream: High in fat and low in carbs, perfect for adding to various keto recipes.
References & Sources
- Consumer Reports of “Keto Flu” Associated With the Ketogenic Diet-https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7082414
- Implementing a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30289048/
- Role of Ketogenic Diets in Neurodegenerative Diseases (Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease)- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6356942/
- The Three-Month Effects of a Ketogenic Diet on Body Composition, Blood Parameters, and Performance Metrics in CrossFit Trainees: A Pilot Study- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29910305/
- Energy Intake and Satiety Responses of Eggs for Breakfast in Overweight and Obese Adults—A Crossover Study- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7432073/
- USDA FoodData Central Nuts & Pecans- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170182/nutrients
- USDA FoodData Central Nuts, Walnuts, English- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170187/nutrients
- USDA FoodData Central Seeds, Chia Seeds, Dried- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170554/nutrients
- USDA FoodData Central Raspberries, raw- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167755/nutrients
- USDA FoodData Central Strawberries, raw- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167762/nutrients


